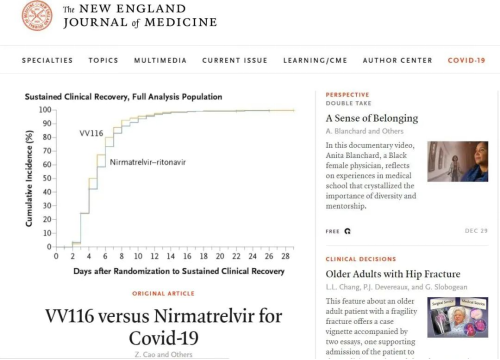
On December 29, the world's leading medical journalThe New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) published online the phase III registration clinical research (NCT05341609) result of comparing nucleoside drug VV116 (JT001) for oral treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) with the combination drug of Nirmatrelvir–Ritonavir (PAXLOVID). The result, applied to the primary treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 patients with progression to severe COVID-19 with the high-risk element of death, indicates that noninferiority is reached at the research endpoint and that patients receiving VV116 treatment perform similarly or even better in recovering compared with PAXLOVID. In addition, the VV116 group consumes less time in clinical recovery and performs better in safety.
Led by Ruijin Hospital and the Shanghai Virus Research Institution, this research was jointly conducted by Renji Hospital, Xinhua Hospital, and Tongren Hospital by coordinating with Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shuguang Hospital affiliated with Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, and Shanghai Pudong Hospital. It is the first Phase III head-to-head clinical trial of oral small-molecule antiviral drug targeting Chinese patients infected with COVID-19 during the Omicron variant surge. Zhao Ren, vice president of Ruijin Hospital, served as the corresponding author. Academician Ning Guang, president of Ruijin Hospital, Gao Yuan at the affiliated Renji Hospital, as well as Xu Yiping and Xie Qing at Ruijin Hospital contributed as the co-authors. Cao Zhujun and Gao Weiyi at Ruijin Hospital are the co-first authors.
This research contributes as an important scientific achievement during the first half of 2022. Amid the fight against Omicron in March 2022 Shanghai, Ruijin Hospital completed designated hospital transfers and admission of infected patients within 48 hours efficiently. Furthermore, Ruijin Hospital acted in a timely manner to send 21 medical teams to join the treatment conducted in designated hospitals and mobile cabin hospitals while completing multiple tough tasks including nucleic acid tests. In the middle of intensive clinical treatments, the medical staff strived to complete the w phase III, noninferiority, observer-blinded, randomized controlled clinical trial of VV116 with 822 participants enrolled.

“Enrolled COVID-19 patients came from the designated hospitals in the northern hospital area of Ruijin Hospital and mobile cabin hospitals operated and managed by Ruijin Hospital,” Zhao Ren, vice president of Ruijin Hospital, said. “The fever clinic in the headquarters of Ruijin Hospital is the earliest standardized fever clinic to meet the management requirement of ‘completing the six major processes of testing, inspection, payment, treatment, prescription, and observation without leaving the fever clinic’ in Shanghai at the early stage of the pandemic. In addition, the fever clinic is equipped with the P2 lab to complete the nucleic acid tests rapidly within 40 minutes. The virus lab of Ruijin Hospital has a daily testing capacity of 15,000 tubes on average to carry out COVID-19 PCR tests. The smooth enrollment of participants in the VV116 clinical trials gives credit to the clinical admission and lab testing capability guaranteed by the fever clinic and the virus lab of Ruijin Hospital.”
Thanks to its multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment team and strong capability in clinical treatment, Ruijin Hospital has allocated multi-level diagnosis and treatment teams in designated hospitals, including the hospital expertise team and the multidisciplinary clinical treatment team. These teams oversee the clinical observation and treatment of participants in clinical trials to ensure medical safety. The expertise team is led by Qu Jieming, Chairman of the Chinese Thoracic Society of Chinese Medical Association and Party Secretary of Ruijin Hospital. Qu leads the hospital expertise team in treating patients while supervising the treatment of severe COVID-19 patients through remote chatting and visualization system of bedside consultation. The multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment team is composed of medical care members from multiple disciplines of clinical care, nutrition, and psychology. Meanwhile, the team leader takes good care of trial participants to ensure that they stay healthy physically and mentally to fight the discomfort and anxiety caused by the infection. Thus, the participants have been cooperating smoothly with the team to complete all crucial clinical trial processes.
An efficient emergency command system is essential to win a battle effectively. During the flight against COVID-19, Ruijin Hospital has been shouldering the tough tasks covering different locations and schedules, including general treatment and special treatments in mobile cabin hospitals and designated hospitals. In fact, the medical staff at Ruijin Hospital are also facing the pressure of completing multiple important scientific tasks, thus attaching importance to the efficient command system of the hospital. Specifically, Ning Guang, president of Ruijin Hospital, has been leading the team to serve at the operation and management command center of the hospital for three consecutive months. Medical resources including all hospital staff, supplies, facilities, and spaces have been coordinated and dispatched in an orderly way during the daytime while discussions on scientific research have proceeded continually in a timely manner at night. Particularly, the online meeting for updates on the VV116 clinical trial has been held at 8:00 p.m. punctually every night.
“Thanks to all the people sharing the same goal on the same path, we are able to complete this research finally,” Ning Guang, Academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering and president of Ruijing Hospital said. “Today, the research result published inThe New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM)proves that the clinical curative effect of VV116 is nothing less than that of PAXLOVID. I sincerely appreciate the whole team’s cautious and conscientious working and generous contributions. Now that the pandemic policy in China comes across a turning point, the door of the country is opening to the outside world again. Our research achievement has not only provided valuable data and experience to the global R&D and clinical application of anti-coronavirus small molecule drugs but also contributed to China’s fight against the pandemic.”

