Academician Fan Xianqun from the Department of Ophthalmology of the Ninth People's Hospital affiliated with SJTUSM took the lead and joined forces with Beijing Children's Hospital affiliated with Capital Medical University, Guangzhou Women and Children's Medical Center, Xinhua Hospital affiliated with SJTUSM, the Third Medical Center of the PLA General Hospital, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, and other national centers of retinoblastoma diagnosis and treatment. They conducted the world's first multi-center prospective randomized controlled study on intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma. This ten-year study shows that super-selected intra-arterial chemotherapy significantly improves the globe salvage rate of children with advanced retinoblastoma and reduces the systemic side effects of chemotherapy. The research results were recently published inThe Lancet Child & Adolescent Health.
Research Background
Retinoblastoma is the most common type of malignant eye tumor in children. 95% occurs in infants and toddlers under 3 years old. It can cause blindness, disability, and even death. It is the most serious and harmful eye disease in children. In 2019, five national ministries and commissions established it as one of the top ten major diseases in Children to be treated and managed in the first batch.
Eye globe enucleation combined with external radiation therapy was once the first-line treatment option for retinoblastoma. The children lose their globes and external radiation therapy causes serious side effects such as second malignant solid tumors and orbitofacial hypoplasia. In the late 1990s, the vincristine-etoposide-carboplatin (VEC) systemic intravenous chemotherapy (SIC) program was applied to treat retinoblastoma, achieving a transition from globe removal to globe salvage treatment. However, the intraocular drug concentration of SIC is low, and the tumor recurrence rate and the globe removal rate remain high. SIC’s serious side effects lead to complications such as myelosuppression and lung infection. To solve this clinical problem, Academician Fan Xianqun's team carried out super-selected intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma. Intubated through the femoral artery, the catheter passed through abdominal aorta-thoracic aorta-common carotid artery-internal carotid artery with a 0.43mm microguide. A wire-guided 0.57mm microcatheter was inserted into the ophthalmic artery. The chemotherapy drugs entered the ophthalmic artery through the catheter and then reached the tumor through the central retinal artery. For children under 3 months old or whose ophthalmic artery diameter is less than 0.65 mm, interventional chemotherapy with balloon dilatation and occlusion was performed. For patients with ophthalmic artery variations, interventional chemotherapy by external carotid artery bypass cannulation was carried out, and a system of intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma was established. Intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma requires a small dosage of drugs and high intraocular drug concentration. It has a strong killing effect on tumors and mild systemic side effects. However, surgeries like this are complicated and may lead to serious complications such as ophthalmic arterial stenosis or occlusion and retinal choroidal atrophy.
Due to the absence of evidence-based medical (EBM) evidence since the launch of super-selected intra-arterial chemotherapy, there has been considerable controversy in the world about the treatment options of intra-arterial chemotherapy and systemic intravenous chemotherapy for retinoblastoma. This has also caused confusion among clinicians.
To solve clinical problems and clear international controversies, Fan led the team to confront the difficulties. With the support of the Special Project of the National Health Industry in 2013, Fan's team conducted the world's first prospective multi-center RCT study on the efficacy and safety of intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma. This study lasted for nearly ten years and provided high-level EBM evidence for treatment plans for retinoblastoma.
Research result
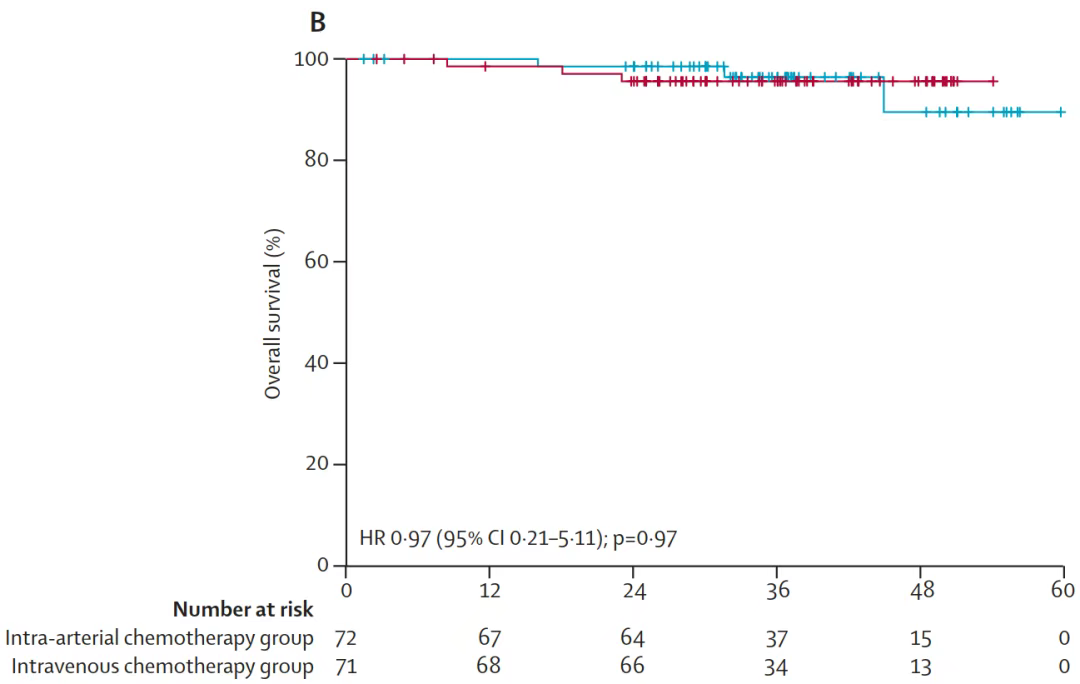
The study is an open-label, multi-center, randomized controlled clinical trial conducted in six hospitals in Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Changsha. The study mainly included children with new-onset unilateral group D or E retinoblastoma and children without clinical high-risk factors. They were randomly divided into the intra-arterial chemotherapy group and the systemic intravenous chemotherapy group. They completed an intra-arterial or intravenous chemotherapy cycle every four weeks. The primary outcome was 2-year progression-free globe salvage rate. The secondary outcome was survival rate, objective response rate, and recurrence rate. Severe adverse events likely to be related to treatment were also recorded. The study selected eligible patients (median age 23·6 months [IQR 14·0–31·9]) with diagnosed retinoblastoma at median follow-up of 35·8 months (IQR 28·4–43·0). The result shows that the 2-year progression-free globe salvage rate was 53% in the intra-arterial chemotherapy group and 27% in the intravenous chemotherapy group. The overall globe salvage rate of the intra-arterial chemotherapy group was significantly higher than that of the intravenous chemotherapy group.
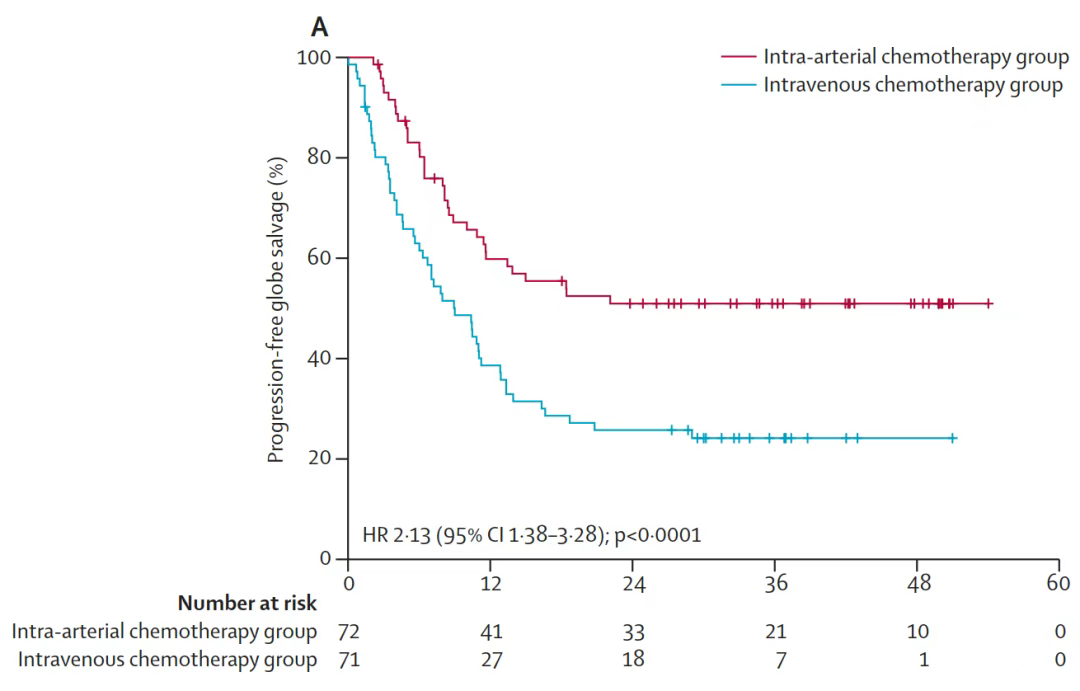
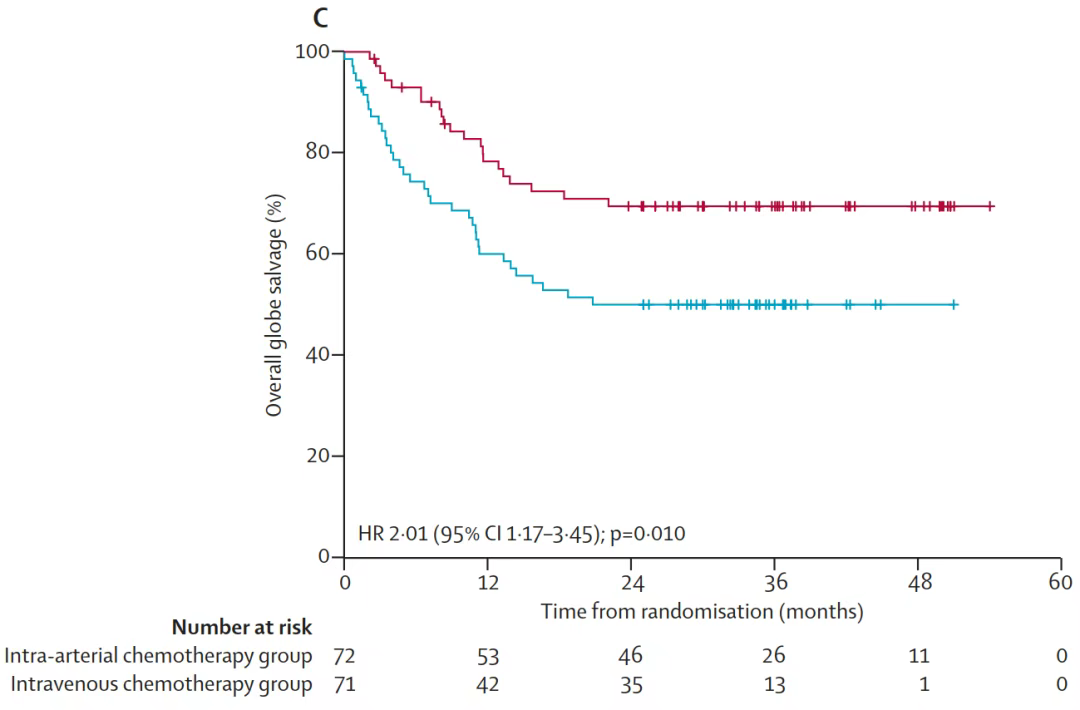
The overall survival rate and recurrence rate of the two groups had no significant difference. The objective response rate of the intra-arterial chemotherapy group was significantly higher than that of the intravenous chemotherapy group.
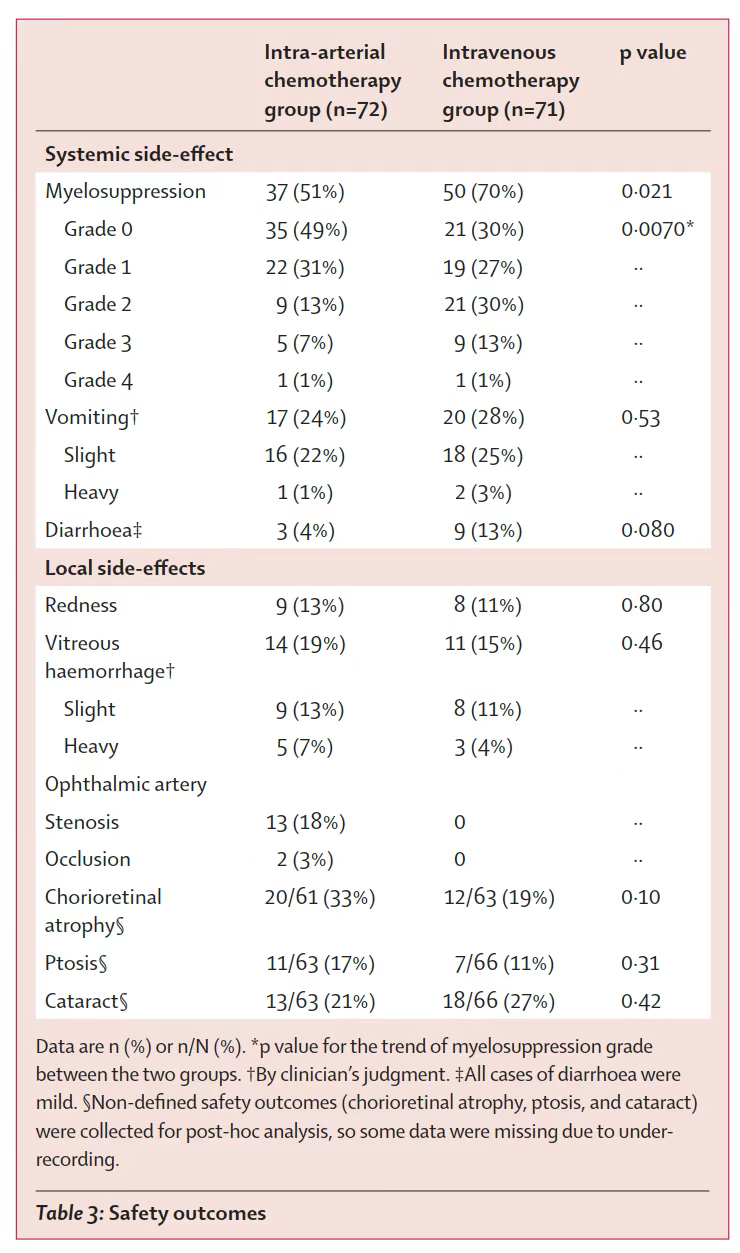
In terms of safety outcomes, no group had severe or fatal complications. The most common systemic complication wasmyelosuppression. Myelosuppression was less common in the intra-arterial chemotherapy group than in the intravenous chemotherapy group ([51%] vs [70%]) and less severe (p=0·0070). There was no significant difference in the occurrence rate of local complications such as vitreous hemorrhage, cataract, and ptosis. In the intra-arterial chemotherapy group, 3% of patients had ophthalmic artery occlusion.
Conclusion
The world's first RCT study on the efficacy and safety of intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma shows that intra-arterial chemotherapy significantly improves globe salvage rate of children with advanced retinoblastoma compared with intravenous chemotherapy without affecting the overall survival rate, while significantly reducing systemic complications. Intra-arterial chemotherapy can be the top treatment option for children with unilateral advanced retinoblastoma.
Academician Fan Xianqun from the Department of Ophthalmology of the Ninth People's Hospital affiliated with SJTUSM is the general leader of the research project and the final corresponding author of the article. Professor Jia Renbing from the Department of Ophthalmology of the Ninth People's Hospital, Professor Zhao Junyang from Beijing Children's Hospital affiliated with Capital Medical University, Professor Zhang Jing from Guangzhou Women and Children's Medical Center, Director Ji Xunda from Xinhua Hospital affiliated with SJTUSM, Director Yang Xinji of the Third Medical Center of the PLA General Hospital, and Director Tan Jia of Xiangya Hospital of Central South University are the co-corresponding authors. Dr. Wen Xuyang from the Department of Ophthalmology of the Ninth People's Hospital is the first author. Deputy Chief Physician Fan Jiayan, Deputy Chief Physician Jin Mei, Dr. Jiang Hua, Dr. Li Jiakai, and Deputy Chief Physician Han Minglei are the co-first authors.
Corresponding Author

Academician Fan Xianqun
Academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, Distinguished Professor of Yangtze River Scholars, expert in ophthalmology, chair professor of SJTU, and member of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. He is currently the vice president of SJTU, chancellor of SJTUSM, director of the Shanghai Key Laboratory of Orbital Diseases and Ocular Oncology, and leader of the Department of Ophthalmology at the Ninth People's Hospital affiliated with SJTUSM. He is also President of the Asia-Pacific Society of Ocular Tumor and Pathology, Fellow of the Academia Ophthalmologica Internationalis (AOI), Fellow of the Royal College of Ophthalmologists (UK), and Honorary Fellow of the Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh. Fan has been in charge of scientific research projects such as Basic Science Center Program, Major Program, and Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation, National Key R&D Programs, Project 863, and Special Project of National Health Industry. The corresponding author has published more than 200 SCI papers in journals such as Cell Stem Cell, Mol Cell, Sci Adv, and Ophthalmology. He presided over the formulation of nine guidelines, authorized 26 patents, and achieved four results transformations. As the first accomplisher, Fan won the second prize in the National Award for Science and Technology Progress twice, and the first prize for the Shanghai Science and Technology Progress Award three times. He was also the winner of the Ho Leung Ho Lee Science and Technology Progress Award, the first Innovator Award of the Asia-Pacific Academy of Ophthalmology, and the De Ocampo Lecture Award, the highest award to ophthalmologists from the Asia-Pacific region for their excellent academic achievements.
First author

Dr. Wen Xuyang
Attending physician at the Department of Ophthalmology, Ninth People's Hospital affiliated with SJTUSM, specializing in clinical and basic research on ocular tumors and ocular vascular diseases. Selected as “Medical Garden Rising Star" in Shanghai, he presided over two National Natural Science Foundation projects, one special project of the Shanghai health industry, and participated in special projects of the National Health Industry, and Shenkang Major Clinical Research. He has published 15 SCI papers as the first and corresponding author (including co-authors) in international academic journals such asLancet Child Adolesc Health, Ophthalmology, and Nucleic Acids Res, including 11 Q1 papers. He has three authorized invention patents and two utility model patents.

