On 25 May, 2022 (US Eastern Standard Time), the Science Advances journal publishes online the “Differential Metabolic Requirement Governed by Transcription Factor c-Maf Dictates γδT17 Effector Functionality in Mice and Humans”, the joint research paper by Professor Chen Fuxiang research group with clinical laboratory of the Ninth People’s Hospital affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine and Professor Jun Yan of University of Louisville of America. This essay reveals the regulation mechanism of immune metabolism of special immune cellγδ T, providing a new clue to the fundamental researches and committed differentiation mechanism ofγδ T cell biology, as well as new thinking for immunotherapy of clinical diseases (e.g. tumor).

In vivo, the immune system is provided with vital immune functions including immunity defense, immunity surveillance, immunity homeostasis, etc. The immune system is composed of immunity organs, immunity cells and immunity molecules, of which, the immunity cells, e.g. T-cell, play a vital role. T-cell can express T cell receptor, TCR to identify antigen and mediate immune response, and the T-cells can, by difference of their TCR peptide chain structure, be classified as αβT cell and γδ T cell. Hence, of T lymph cells, besides the commonly seen αβT cells, there are also a group of special cell mass, that is, the γδ T cell of TCRγδ. Despite a small amount of γδ T cells found in recent studies, the γδ T cells are widely distributed in vivo, especially in mucosal tissues, and exert very important role in physiological or pathological process.
By difference of their secretary cytokine, γδ T cells can be further divided into γδ T17 cell secreting interleukin-17 and γδ T1 secreting γ-interferon. It is jointly discovered by Professor Chen Fuxiang research group and Professor Jun Yan with University of Louisville in their cooperation that, difference exists between γδ T1 cell and γδ T17 cell in terms of primary metabolic pathways: the γδ T1 cell relies mainly on glycolysis for energy supply, while the γδ T17 cell relies on glutamine metabolism and tricarboxylic acid (TCA) circulation. In addition, the iso-citric dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2), the metabolic enzyme in TCA circulation has over-expression in γδ T17 cells. By dint of small interfering RNA (siRNA)technology and chronic virus transfection technology, it is discovered through studies that, of the γδ T cell secretory cytokine functions, IDH2 plays the role as key metabolic enzyme.
It is also found by the research that, the transcription factor c-Maf also has over-expression in γδ T17 cells, and moreover has co-expression with RORγt, the core transcription factor for regulating interleukin-17. By further constructing conditional knockout mouse experiment, the research reveals that, transcription factor c-Maf can, in γδ T17 cells, directly regulate the key metabolic enzyme IDH2 to mediate the secretion of interleukin-17. Additionally, this research further finds that the mTORC2 signal pathways, as upstream signal of c-Maf, are of critical importance to γδ T17 cell expression of c-Maf and secretion of interleukin-17. These research results provide new clue for further revealing γδ T cell biology and committed differentiation mechanism.
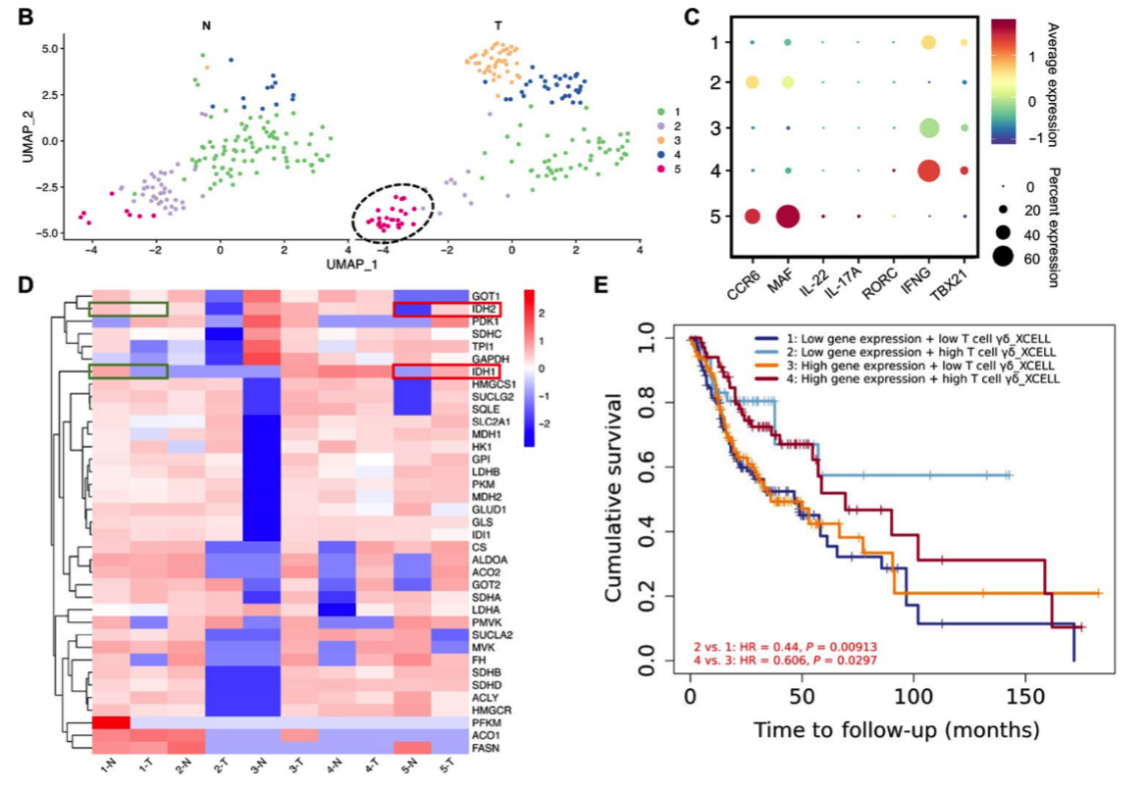
In the meantime, the partnership team, focusing further on oral squamous cell carcinoma, a clinical specialty disease of the Hospital, conduct diagnosis on γδ T cells in oral squamous cell carcinoma using single cell sequencing technology. The research discovers that, γδ T17 cells of certain proportion exist in the tissues of oral squamous cell carcinoma, and that, these cells have over-expression of c-Maf. The research team also analyzes γδ T cells and c-Maf expression’s role on the patients of oral squamous cell carcinoma, and finds that, the contrast group of patients with highly infiltrating γδ T cells and having c-Maf low-expression witness higher survival. These research results provide new thinking for clinical immunity treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Doctor Chen Xu with Professor Chen Fuxiang research team of the Ninth People’s Hospital affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine is the first author of this essay, Professor Chen Fuxiang and Professor Jun Yan with University of Louisville are the correspondent author of this essay.

