Center for Single-Cell Omics (CSCOmics)
Date:2019-12-13 show:
The Center for Single-Cell Omics (CSCOmics) at Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine was founded in 2019 to become a leader in the development of cutting-edge laboratory and computational technologies for analyzing the various levels of genetic information transfer in single cells. The CSCOmics is an international research center where we working as teams trying to utilize new, single-cell technology for improving human health. Single-cell approaches are critically important in studying the molecular basis of the cell fate decisions that drive age-related diseases, such as cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases, as well as cancer.

Center for Single-Cell Omics (CSCOmics) was officially opened in November 2019
and is part of the Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine
Genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics and now many other types of “omics” analysis have revolutionized the biomedical sciences. Omics technologies have facilitated the development of biomarkers to define pathological phenotypes, facilitate the monitoring of disease progression and treatment response, and the unraveling of the molecular pathways underlying the disease, which in turn will lead to new targets for therapy.
Over the past decade the application of omics technologies has decisively shifted from analyzing whole tissues or cell populations to single cells. This is a consequence of the realization that seemingly identical cells in a tissue can be very different, biologically and clinically. This heterogeneity has important implications for studying the molecular basis of cell fate decisions that drive disease, not only cancer but other complex diseases as well, such as cardiovascular disease and neurodegeneration.
It is for these reasons that studying human disease at the level of bulk populations of cells is now generally recognized as insufficiently accurate to identify the causes of disease and the development of new diagnostic and therapeutic interventions. The analysis of different layers of cellular information, from the genome and epigenome to the transcriptome, proteome and metabolome levels, will help to identify and understand differences between cell types and cell subpopulations. This in turn is crucial, for example, in discovering how cancer spreads or how specialized cells can be optimally utilized in regenerative medicine.
Single-cell technologies
Ample progress has been made with single-cell technologies and investigators have begun to combine multiple omics levels in the same single cells to increase information content of one and the same assay. This so-called single-cell multi-omics approach is considered important because of the current lack of insight into the relationship between the different levels of molecular information in a cell. For example, we do not know the impact of mutations in a cell on its transcriptome and gene expression profiling can give you very different results than analyzing expression of the same genes at the protein level.
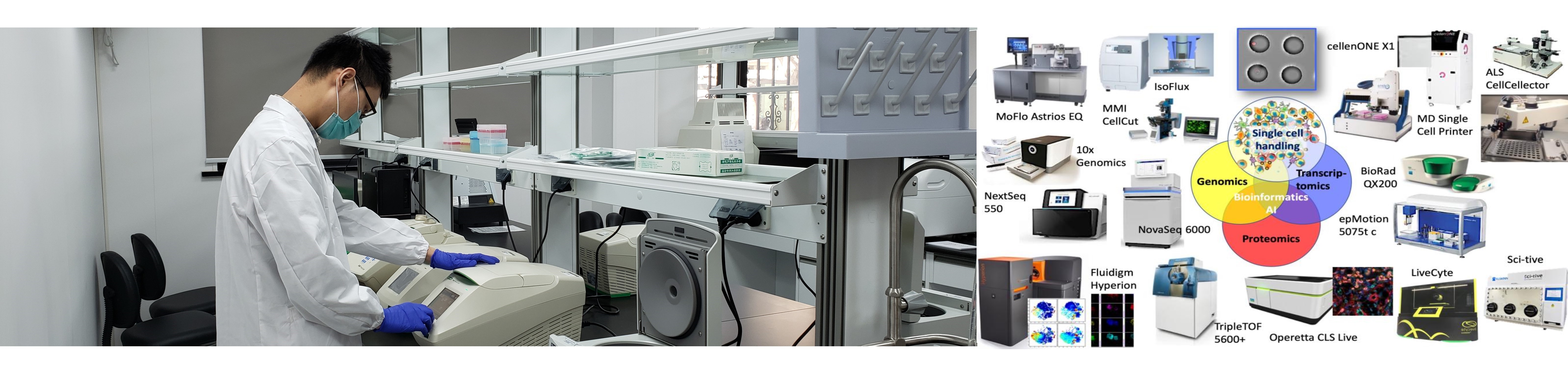
Single-cell multi-omics is extremely powerful, but technically challenging. CSCOmics integrates various single-cell technologies and will provide investigators with cutting-edge laboratory and computational tools. CSCOmics will also be leading the development of novel, multi-omics single-cell approaches, such as 3-D intra-tissue single-cell analysis, as well as the use of artificial intelligence, machine learning analysis of the single-cell data. We are developing and constantly improving standardized and robust workflows to process clinical samples, study their individual cell compositions in-depth at different omics levels, and analyze the data in an integrated manner.
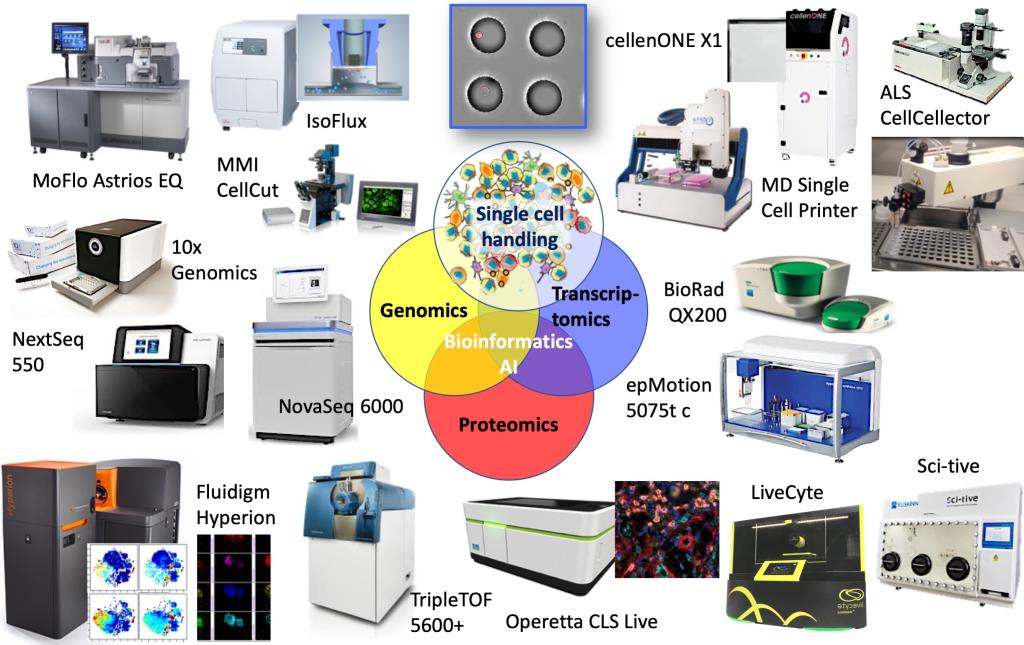
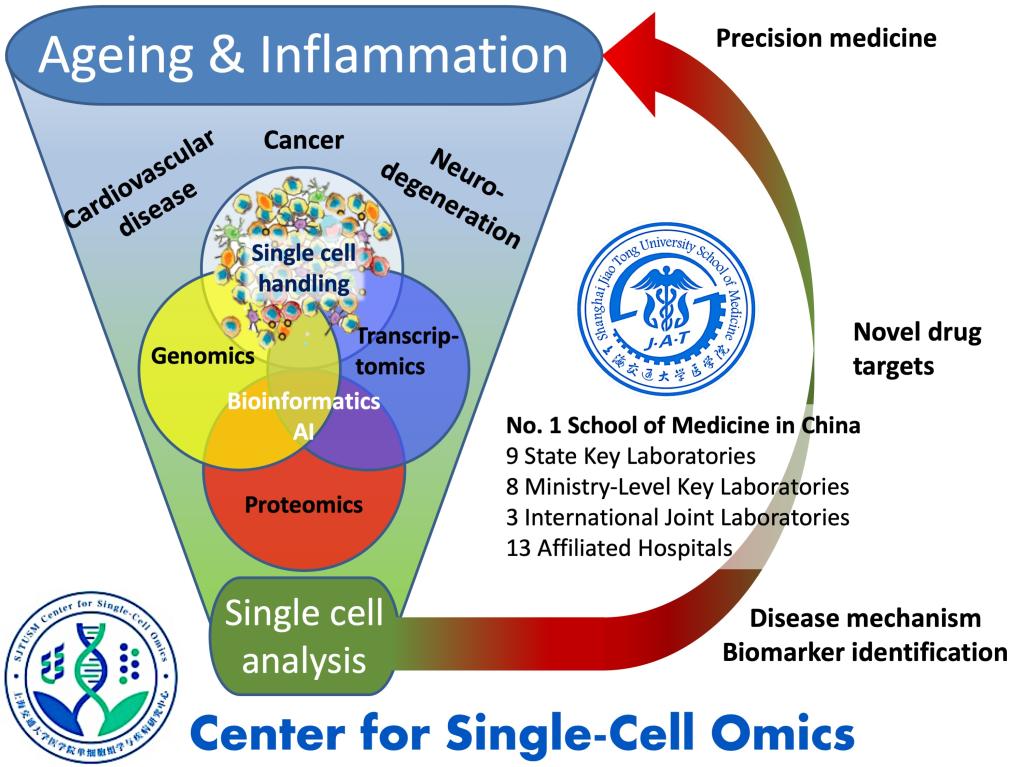
CSCOmics hosts four Single-Cell Cores for Single-Cell Identification & Isolation, Genomics, Mass Spec (for single-cell proteomics and metabolomics) and Bioinformatics, thereby providing CSCOmics’ investigators with a palette of cutting-edge single-cell services. CSCOmics closely connects to the thirteen affiliated hospitals of the SJTU School of Medicine to use the novel, single cell information streams for studying mechanisms of human age-related diseases and developing new generations of biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Hence, the key focus of the center will become the translation of basic science findings into novel interventions to prevent, delay or reverse aging-related chronic disease.
Age-related diseases
The specific diseases with unmet medical need we are particularly interested to study at the single-cell level are cancer, cardiovascular disease and neurodegeneration. Using high-precision, single-cell technology we will establish pipelines for identifying common multi-omics targets across diseases and developing novel interventions, including biomarkers to precisely tailor their use towards individual patients. We aim to unravel the molecular and cellular basis of treatment resistance at single-cell resolution, the common factors among age-related diseases, and the influence of host cellular microenvironments. This should deliver highly precise biomarkers to stratify patient populations for new therapies that are increasingly effective and therefore will promote healthy aging.

